Menu

Dr. Sanjay Barik
Knee & Shoulder Surgeon
Meet Our Doctor

Dr. Sanjay Barik
Orthopedic and Joint Replacement Surgeon
Dr. Barik's Orthocare Clinic
- MBBS
- MS - Orthopaedics
Dr. Sanjay Barik is an experienced Orthopedic Doctor in Ramdaspeth, Nagpur. He is a qualified MBBS Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery, MS – Orthopaedics.
Hip Replacement In Bhandara
- Home
- Quick Links
- Hip Replacement In Chandrapur
Hip replacement, also known as hip arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which a damaged or diseased hip joint is replaced with an artificial joint, called a prosthesis. This procedure is typically performed to relieve pain and improve the function of the hip joint in cases of severe arthritis, injury, or other conditions that affect the hip.
Indications
- Osteoarthritis: Degeneration of the joint cartilage and the underlying bone.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: Inflammatory joint disease.
- Avascular necrosis: Loss of blood supply to the hip joint, leading to joint deterioration.
- Hip fractures: Especially in older individuals.
- Other hip conditions causing significant pain and disability.
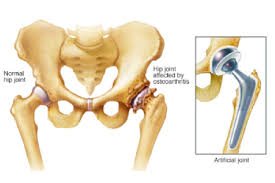
Procedure
- Thus, The damaged parts of the hip joint are removed and replace with artificial components.
- Firstly, The hip prosthesis typically consists of a metal socket, a plastic or metal liner, and a metal femoral component with a stem that is inserted into the femur.
- Once, The artificial components may be cemented into place or may rely on the bone's natural growth to attach to the prosthesis (uncemented).
Recovery:
- Physical therapy is a crucial part of the recovery process to regain strength, flexibility, and mobility.
- Patients are often encouraged to start walking with the help of crutches or a walker shortly after surgery.
- Full recovery can take several weeks to months, depending on the individual and the specific surgical approach use.
Complications:
- While hip replacement surgery is generally safe, complications can occur, including infection, blood clots, dislocation of the hip joint, and implant wear.
- Modern surgical techniques, materials, and postoperative care have significantly reduced the risk of complications.
Types of Hip Replacement:
- Total Hip Replacement (THR): Replacing both the ball and socket of the hip joint.
- Partial Hip Replacement (Hemiarthroplasty): Replacing only the femoral head, often used in cases of hip fractures.
Advancements:
- Advances in materials and surgical techniques have improved the durability and longevity of hip prostheses.
- Minimally invasive surgical approaches have been developed to reduce the size of incisions and potentially speed up recovery.
Postoperative Care:
- Patients are usually given instructions on activities to avoid, such as certain movements and positions that could jeopardize the new joint.
- Regular follow-up appointments with the orthopedic surgeon are essential to monitor the healing process.


