
Dr. Sanjay Barik
Knee & Shoulder Surgeon
Meet Our Doctor

Dr. Sanjay Barik
Orthopedic and Joint Replacement Surgeon
Dr. Barik's Orthocare Clinic
- MBBS
- MS - Orthopaedics
Ligaments Injuries In Nagpur
Ligament injuries occur when the strong ligaments that connect bones to bones stretch or tear. Think of ligaments as strong ropes that hold bones in place and provide stability to joints. These injuries often occur during sudden movements, falls, or twists, and especially affect joints such as the knees and ankles. The result is often pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the affected area. The severity of ligament injuries can range from a mild contusion to a more severe tear. To recover, it is important to give your body time to heal, take appropriate therapeutic measures, and possibly seek physical therapy. This allows damaged ligaments to heal and regain strength, restoring stability to the joint and allowing comfortable movement.
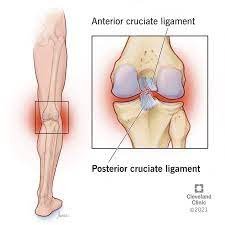
Different types of Ligament Injuries
1.Sprains: Ligament strains occur when a ligament is stretched or torn but not completely severed. Sprains are often classified by severity, from mild (grade 1) to moderate (grade 2) to severe (grade 3).
2. Partial tear: A partial tear means that part of the tape is damaged, compromising the integrity of the tape, but it is not completely torn. The degree of tearing varies and can affect the functionality of the band.
3. Complete tear: A complete ligament tear occurs when the ligament is completely severed and loses its continuity. This type of injury can have a significant impact on joint stability and function.
4. ACL (Anterior Cruciate Ligament) Injury: The ACL is an important ligament in the knee. Anterior cruciate ligament injuries often involve significant tears and often occur during activities that involve a sudden stop, change of direction, or direct impact.
5. MCL (Medial Collateral Ligament) Injury: The MCL is a ligament on the inside of the knee. MCL injuries often occur from a direct blow to the outside of the knee or a twisting motion that causes a twist or tear.
6. Posterior Cruciate Ligament Injury (Posterior Cruciate Ligament): The posterior cruciate ligament is located on the back of the knee and is less frequently injured than the anterior cruciate ligament. PCL injuries often occur due to direct impact or hyperextension to the front of the knee.
7. LCL (Lateral Collateral Ligament) Injury: The LCL is located on the outside of the knee. LCL injuries are less common than MCL injuries and are usually caused by forces pushing the knee inward.
8. Ankle ligament injuries: Ankle ligament injuries, such as the anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL), are common and often caused by rotating or twisting the ankle.
9. Wrist Ligament Injury: Wrist ligament injury can occur as a result of a fall or impact and can affect stability and movement of the wrist.
10.Shoulder Ligament Injury: Shoulder ligaments, such as the acromioclavicular ligament (AC), can be injured during falls or trauma, causing shoulder instability.
11. Hip Ligament Injuries: Hip ligament injuries occur due to sudden movement or impact and can affect the stability of the hip joint.
Treatment for Ligament Injuries
If you have a minor ligament injuries. For example, a mild ankle sprain may be treatable at home. Orthopedic surgeons often recommend a RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) therapy protocol. However, for more severe tears, you will need to see a doctor who will perform several tests to make a diagnosis and provide appropriate treatment.
The treatment plan for ligament tears depends on the location of the tear, the severity of the injury, and the patient’s tolerance for various treatment options. A cast or crutches may be required, and surgery may be required to repair torn ligaments. After surgery or immobilization, you may need physical therapy and rehabilitation to return to your pre-injury condition.
Although some ligament tears are relatively minor, they should not be taken lightly. If the pain or swelling does not go away within 24 to 72 hours, if you are unable to put weight on the affected area, or if your symptoms worsen, seek immediate medical attention.
RICE Therapy Protocol
Rest: Do not put weight on the injured body part or lift anything with the injured wrist, elbow, or shoulder for at least 1 to 2 days.
Ice: Apply ice or cold packs to the affected area for 10 minutes every 30 minutes to 1 hour for the first 2 to 3 days. Wrap the ice cream in a thin damp cloth. Do not apply ice directly to your skin.
Compression: Wrap the injury with an elastic bandage or use a compression sleeve appropriate for the specific injury type.
Elevation: Keep the injured area above heart level. The easiest way to do this is to lie down and raise your legs or arms slightly above you.
Best Orthopedics Clinics
Dr. Barik Ortho Care Clinic is the Best Ortho clinic in Nagpur. Dr. Barik is an exceptional orthopedic doctor who consistently demonstrates a high level of expertise and commitment to patient care. With an extensive background in orthopedics, Dr. Barik combines skill and compassion, making a significant positive impact on the well-being of his patients. His thoroughness in diagnosis, clear communication, and tailored treatment plans reflect his dedication to ensuring the best possible outcomes for those under his care.
Causes of Ligament Injuries
- Trauma and Impact: Direct trauma or impact to a joint, such as a fall or collision, can cause ligament injuries. Common examples include traffic accidents and sporting events.
- Twisting or Hyperextension: Sudden, violent twisting or hyperextension of a joint can cause ligaments to overstretch or tear. This often occurs during sports activities or sudden movements.
- Falls: Falls, especially if you land with your arms outstretched or twist while falling, can cause ligament injuries, especially in the wrists, knees, and ankles.
- Improper Lifting Techniques: Improper lifting of heavy objects can strain and damage the ligaments, especially in the back.
- Repetitive Stress: Excessive or repetitive stress on joints, which occurs frequently during activities such as running and jumping, can gradually cause ligament damage over time.
- Unfavorable Landing: An awkward landing after a jump or fall can lead to ligament damage, especially if the joint is unstable.
- Sudden Stopping or Change of Direction: Sudden stopping or changing direction during sports or physical activity can put undue stress on ligaments and lead to injury.
- Collisions in Sports: In sports that involve physical contact, such as football and soccer, there is a high risk of ligament injury from collisions with other players.
- Poor Muscle Conditioning: When the muscles around a joint are weak or imbalanced, they don’t provide adequate support and the ligaments are more susceptible to injury.
- Genetic Factors: Some people may have a genetic predisposition to lax ligaments, making them more susceptible to injury from even minor trauma.
- Age: As we age, our ligaments lose some of their elasticity and strength, making them more susceptible to injury during daily activities.
- Previous ligament injuries: People with previous ligament injuries may be at increased risk of reinjury due to residual muscle weakness and changes in joint mechanics.
Common Process for Ligament injuries
Its depends on doctor and patients conditions at that moments but these are some common practices that are carried out
X-ray. A diagnostic test that uses an invisible beam of electromagnetic energy to produce images of internal tissues, bones, and organs on film to rule out bone injuries instead of, or in addition to, ligament injuries.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). A diagnostic procedure that uses a combination of large magnets, radiofrequency waves, and a computer to create detailed images of organs and structures inside the body. It can often detect damage or disease to the bone or surrounding ligaments or muscles.
Arthroscopy. Minimally invasive diagnostic and therapeutic procedures for the treatment of joint diseases. This procedure uses a small, lighted optical tube (arthroscope) that is inserted into the joint through a small incision in the joint. An image of the inside of the joint is projected onto a screen. Used to evaluate degenerative and/or arthritic changes in joints. To detect bone diseases and tumors. Identify the cause of bone pain and inflammation.


