
Dr. Sanjay Barik
Knee & Shoulder Surgeon
Meet Our Doctor

Dr. Sanjay Barik
Orthopedic and Joint Replacement Surgeon
Dr. Barik's Orthocare Clinic
- MBBS
- MS - Orthopaedics
Rheumatologist Nagpur
Rheumatologist deals with Rheumatic diseases or rheumatic diseases include a different group of diseases that primarily affect the joints, muscles, and connective tissues. These diseases are often autoimmune or inflammatory in nature and cause chronic pain, swelling, and stiffness in various parts of the body. Rheumatic diseases have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life and can lead to limitations in mobility and function. Rheumatic disease is a general term that refers to arthritis and several other diseases that affect the joints, tendons, muscles, ligaments, bones, and muscles (arthritis refers to diseases that primarily affect the joints). Rheumatic diseases such as osteoarthritis can destroy cartilage, the hard, soft tissue that protects joints, if not treated properly, causing severe joint pain.
The most common rheumatic diseases include osteoarthritis, the most common form of arthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis, also known as RA. Rheumatoid arthritis is a disease in which the immune system attacks healthy cells. Inflammation, swelling, and pain may occur in multiple joints at the same time.
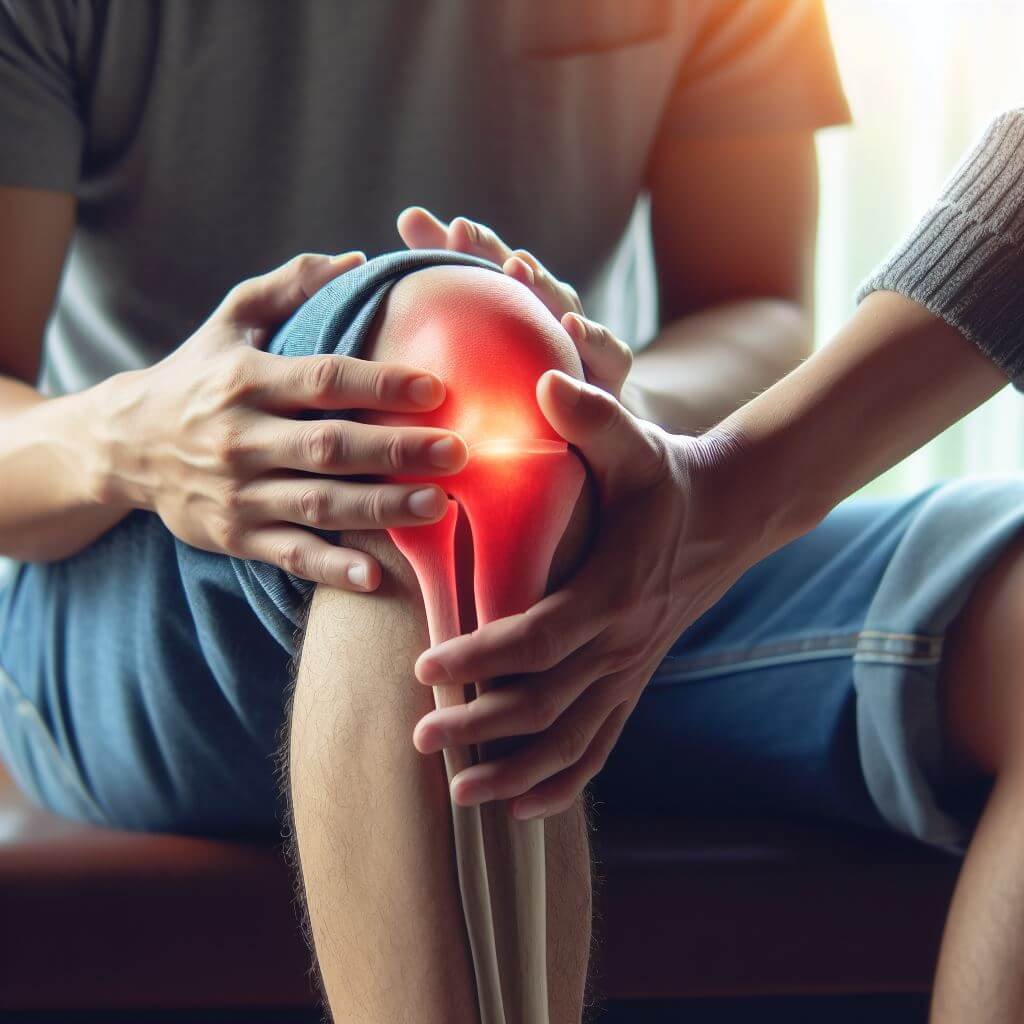
Rhematic is wide term, which include many orthopedics diseases, such as follows:
Now there are more than 200 distinct rheumatic diseases. Among the most common ones are
1. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): RA is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by inflammation of the joints that causes pain, swelling, and ultimately joint damage. Often multiple joints are affected symmetrically.
2. Osteoarthritis (OA): Osteoarthritis is not a purely autoimmune disease, but is a common rheumatic disease that causes degeneration of the articular cartilage and underlying bone. The result is pain and stiffness, which often affects stressed joints.
3. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): SLE is a systemic autoimmune disease that affects various organs such as the joints, skin, kidneys, heart, and lungs. Symptoms range from joint pain to skin rashes to organ dysfunction.
4. Spondyloarthritis: This group of inflammatory rheumatic diseases includes diseases such as Bechtereu’s disease, psoriatic arthritis, and reactive arthritis. These usually affect the spine and peripheral joints.
5. Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA): JIA refers to a group of chronic arthritic diseases that begin in childhood and are associated with persistent joint inflammation. It may affect a child’s growth and development.
6. Systemic Sclerosis (Scleroderma): Scleroderma is characterized by abnormal growth of connective tissue, causing thickening of the skin and damage to internal organs. It can affect the joints, blood vessels, and digestive system.
Polymyalgia Rheumatica (PMR): PMR is an inflammatory disease that primarily affects the shoulders and lower back, causing pain and stiffness. It is often seen in the elderly.
Rheumatic Disorders is hard to know, so the sympotoms of the disorder should not be neglected. These sysmptoms should be examined
Symptoms of rheumatic diseases vary widely depending on the clinical picture, but common features include joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and limited movement. In addition, systemic symptoms and complications may occur. Common symptoms associated with rheumatic diseases include:
1. Joint Symptoms:
Pain: Persistent or recurrent pain in one or more joints is a common symptom. The pain may be aching, throbbing, or sharp.
Swelling: Inflammation can cause swelling in the area of the affected joint.
Stiffness: Stiffness of the joints, especially in the morning or after a period of inactivity, is a feature of many rheumatic diseases.
2. Fatigue:
Chronic fatigue is a common condition that has a significant impact on daily life. This may be related to underlying inflammation or the body’s immune response.
3. Muscle pain and weakness:
Some rheumatic diseases, such as polymyositis and dermatomyositis, can cause muscle pain and weakness.
4. Skin Changes:
Skin symptoms vary and may include rashes, redness, and other abnormalities. Diseases such as lupus and scleroderma often involve skin symptoms.
5. Fever:
Certain rheumatic diseases can cause systemic symptoms, including fever, especially during flare-ups.
6. Morning stiffness:
Persistent morning stiffness lasting more than 30 minutes is a common feature of inflammatory arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms visit Dr. Barik’s Orthocare Clinic now. Dr. Sanjay Barik’s work in Rheumatic research, coupled with his work on innovative diagnostics and treatment protocols, plays an important role in advancing our understanding of this complex disease. His expertise, particularly in creating tailored treatment plans and promoting a holistic, patient-centered approach, emphasizes the importance of a comprehensive and individualized approach to arthritis management.
Let know how to prevent Rheumatic Disorders by doing simples steps
1. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle:
Regular Exercise: Exercise regularly to maintain joint mobility, muscle strength, and overall health. Low-impact exercises such as swimming, walking, and cycling are effective.
Balanced Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grain products, and lean protein. Proper nutrition supports overall health and helps reduce inflammation.
2. Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on your joints, especially weight-bearing joints such as your knees and hips. Weight management is important to prevent diseases such as osteoarthritis.
3. Joint Protection:
Practice joint protection techniques to minimize stress on your joints. This includes using ergonomic tools, avoiding repetitive movements for long periods of time, and maintaining good posture.
4. Avoid smoking: Smoking is associated with an increased risk of certain rheumatic diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis. Quitting smoking can have a positive impact on your overall health.
5. Limit Alcohol Intake:
Excessive alcohol consumption can cause inflammation and increase the risk of certain rheumatic diseases. Moderation is the key to promoting joint health.
6. Regular health check-ups:
Regular health check-ups by your doctor can help detect possible rheumatic diseases early. This is especially important if you have a family history or other risk factors.
7. Protect against infections:
Some rheumatic diseases can be caused by infections. Preventive measures include good hygiene, encouraging vaccinations, and avoiding infectious diseases.
8. Stress Management:
Chronic stress can cause inflammation and worsen symptoms of rheumatic diseases. Stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, and relaxation exercises can help.
9. Use proper body mechanics:
Whether at work or during physical activity, using proper body mechanics can help prevent injury and reduce the risk of musculoskeletal problems.


