
Dr. Sanjay Barik
Knee & Shoulder Surgeon
Meet Our Doctor

Dr. Sanjay Barik
Orthopedic and Joint Replacement Surgeon
Dr. Barik's Orthocare Clinic
- MBBS
- MS - Orthopaedics
Shoulder Fracture In Nagpur
A shoulder fracture occurs when one or more bones within the shoulder joint are damaged. Broken or lacerated collarbone, scapula, or proximal humerus due to trauma. This trauma is often caused by a fall, direct blow, or high-impact accident. The severity and type of fractures vary from hairline fractures to more complex fractures in which bone fragments have been displaced. Symptoms include pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty moving the affected arm. Treatment depends on the specific fracture and may include immobilization with a sling, pain management, and, in severe cases, surgery to realign and stabilize the bone. Physical therapy rehabilitation is often used to restore muscle strength and mobility during the recovery process. Prompt medical attention is important for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
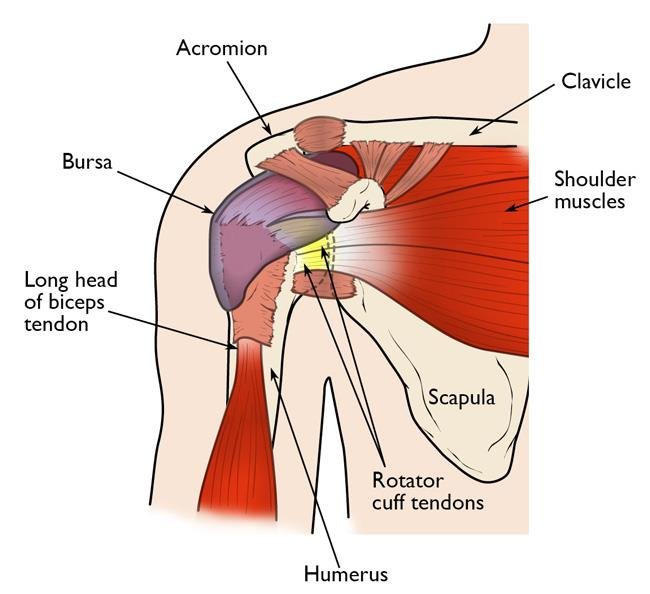
Shoulder Fractures can be of many types, so here are the few main type of the Shoulder fractures occur in general:
Shoulder fractures can affect different bones within the shoulder joint, and the specific type of fracture depends on the location and pattern of the fracture. Here are some common types of shoulder fractures.
1. Clavicle Fractures (Clavicle Fractures): Fractures of the clavicle are common and can occur in different parts of the bone. Often caused by a fall or direct blow from the shoulder. Clavicle fractures can be classified into midshaft fractures, lateral fractures, and medial fractures.
2. Fractures of the scapula (shoulder blade): Fractures of the scapula are less common but can be caused by severe trauma, such as: B. Motor vehicle accident or fall. A scapula fracture can affect the body, neck, or glenoid (the socket part of the shoulder joint).
3. Proximal humerus fracture: Aproximal humerus fracture occurs at the top of the humerus near the shoulder joint. These fractures often involve an anatomical structure known as the greater tuberosity, lesser tuberosity, or surgical humeral neck.
4. Glenoid Fractures: Fractures of the glenoid fossa are rare and affect the fossa portion of the shoulder joint. These can occur in conjunction with other shoulder injuries and affect the stability of the shoulder joint.
5. Humeral Shaft Fractures: Fractures along the humeral shaft (body) away from the shoulder joint may also occur. These fractures can be caused by direct trauma or indirect forces and vary in severity.
6. Acromion Fracture: An acromion fracture is an extension of the scapula bone that runs across the top of the shoulder and can occur due to trauma. These fractures can affect the stability of the shoulder joint.
7. Coracoid Process Fracture: Fractures of the coracoid process, a bony prominence of the scapula, are rare but can occur in conjunction with other shoulder injuries.
8. Cliff fracture: This term is sometimes used to describe a specific type of glenoid fracture in which a portion of the glenoid rim is affected and resembles a cliff-like structure.


