
Dr. Sanjay Barik
Knee & Shoulder Surgeon
Shoulder Replacement
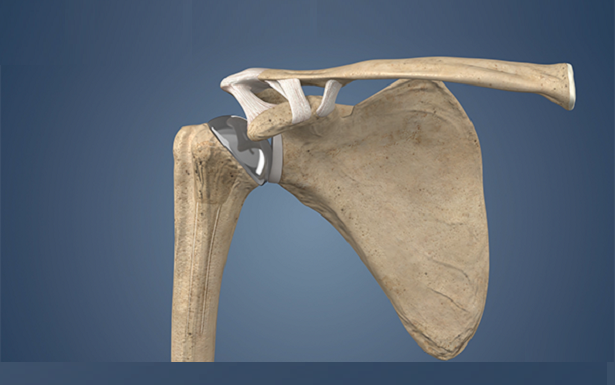
What is Shoulder Replacement
Shoulder replacement surgery aims to alleviate pain and restore function by replacing damaged parts of the shoulder joint with artificial components known as prostheses.
This procedure is typically recommended for conditions such as osteoarthritis, rotator cuff tear arthropathy, avascular necrosis, or rheumatoid arthritis.
Its goal is to reduce pain, enhance strength, improve range of motion, and restore the ability to use the shoulder and arm effectively.
What are the types of shoulder replacements?
- Hemiarthroplasty: This procedure involves replacing only the ball and stem of the shoulder joint. The stem is connected to the ball and articulates with the natural socket.
- Resurfacing Hemiarthroplasty: In this approach, the joint surface of the humeral head is replaced with a cap-like prosthesis, without the addition of a stem.
- Anatomic Total Shoulder Replacement: In this procedure, the arthritic joint is replaced with a highly polished metal ball attached to a stem on the humeral side, along with a plastic cup on the glenoid socket.
- Stemless Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: This type of total shoulder arthroplasty preserves bone by attaching the metallic ball directly to the upper arm without a stem.
- Reverse Total Shoulder Replacement: Here, the joint configuration is reversed, with the metal ball placed where the glenoid socket was, while a plastic cup is attached to the stem and moved to the upper arm bone (humerus).
Shoulder replacement procedures
Your doctor may suggest one of the following shoulder replacement options based on the type of joint damage:
Anatomic Total Shoulder Replacement: This involves replacing both the ball and socket of the shoulder joint with implants that mimic the natural bone shapes.
Reverse Total Shoulder Replacement: In this procedure, both the ball and socket are replaced, but their positions are reversed. The ball is attached to the shoulder blade, while the socket is affixed to the upper arm bone. This option is often recommended when the rotator cuff damage is severe.
Partial Shoulder Replacement: This procedure replaces only the head (ball) of the joint. It’s typically recommended when the damage is limited to the ball side of the joint.
Are there any complications of shoulder replacement surgery?
Shoulder replacement surgery, like any surgical procedure, carries potential risks and complications, including:
- Infection: Minor infections are typically treated with antibiotics, while more severe cases may necessitate further surgical intervention.
- Dislocation: In the case of reverse total shoulder replacement, the implant may dislocate, requiring either closed reduction or surgical revision.
- Prosthesis issues: Components of the prostheses can wear down over time, leading to potential loosening or malfunction, which may require additional surgery.
- Nerve damage: There is a risk of nerve injury during surgery, which can result in temporary or permanent impairment.
- Diabetes-related complications: Patients with diabetes are at an increased risk of wound complications and infections following surgery.
It’s important to discuss these risks thoroughly with your healthcare provider before undergoing shoulder replacement surgery.


