
Dr. Sanjay Barik
Knee & Shoulder Surgeon
Meet Our Doctor

Dr. Sanjay Barik
Orthopedic and Joint Replacement Surgeon
Dr. Barik's Orthocare Clinic
- MBBS
- MS - Orthopaedics
Sports Injury In Mancherial
Sports injuries include a wide range of conditions that result from physical activity and can affect various body structures such as muscles, ligaments, tendons, and bones.
These injuries often occur during sports or exercise and can be classified as acute or chronic. Acute injuries are caused by sudden trauma or impact, such as sprains, strains, fractures, or dislocations, and commonly occur in high-impact sports such as soccer and basketball. Chronic injuries, on the other hand, occur over time due to repetitive stress, overuse, and improper training techniques, leading to conditions such as tendonitis and stress fractures.
To minimize the risk of sports injuries, preventive strategies such as proper warm-up, conditioning, and technical training are essential, and timely and appropriate medical interventions contribute to effective rehabilitation and recovery.
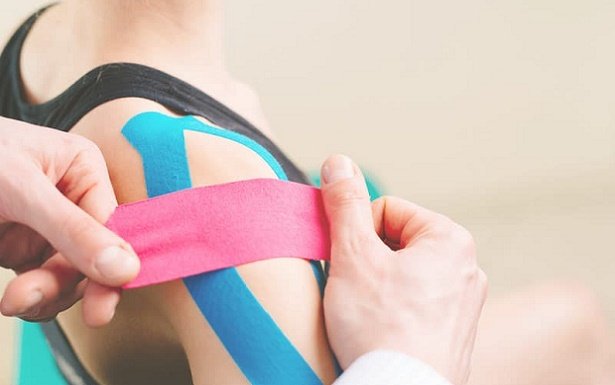
Firstly,The type and severity of sports injuries vary widely depending on the activity, the athlete’s condition, and other factors.Once, The most common sports injuries include muscle injuries, ligament injuries, joint dislocations, and fractures.
Thus, Athletes who play contact sports may be more prone to traumatic injuries, while athletes who perform repetitive motions may develop overuse injuries. Comprehensive injury management includes a combination of immediate first aid, medical evaluation, rehabilitation, and preventative measures to enable athletes to safely return to activity and minimize the risk of future injuries. Thus, Regular monitoring of athlete condition, training to prevent injury, and adherence to proper training techniques are essential parts of promoting a healthy and resilient sports community.
Types of Sports Injury
1. Strains and Sprains:
Muscle Injury: Once, Overstretching or tearing of muscle fibers, often as a result of rapid or forceful movement.
Ligament sprain: Firstly, Stretching or tearing of the ligaments that connect bones to bones. It is usually caused by a sudden twist or impact.
2. Fractures:
Stress Fractures: Therfore, Small cracks in bones caused by repeated stress or overuse.
Traumatic fracture: Thus, A complete or partial fracture caused by direct impact or force.
3. Dislocation: Dislocation of a joint from its normal position. It often occurs during contact sports and high-impact activities.
4. Tendonitis: Tendonitis is usually caused by overuse or repetitive movements and causes pain and swelling.
5. Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae (fluid-filled sacs) that cushion the joints. However, It is often caused by repetitive motion or direct trauma.
6. Concussion: Mild traumatic brain injury caused by a blow to the head in contact sports.
Who can suffer sports injuries?
People suffer Sports Injuries beacause of :
1. Poor Physical Condition: People who lack physical strength and conditioning are more susceptible to sports-related injuries. Decreased muscle strength, reduced endurance, and limited flexibility increase vulnerability.
2. Lack of proper protective equipment: Lack of proper equipment, such as helmets, pads, and braces, increases the risk of impact-related injuries. Protective devices serve as important protection and minimize the severity of possible accidents.
3. Insufficient warm-up and cool-down: Performing physical activity without a proper warm-up can lead to muscle strains and injuries. Skipping your cool-down routine can impede your body’s recovery process and increase your risk of delayed injury.
4. Participation in Contact Sports: Contact sports that involve duels or collisions generally increase the risk of injury. The physical nature of these sports can expose participants to fractures, dislocations, and concussions.
5. Dynamic and High Impact Activities: Engaging in activities that require jumping, running, changing direction, or sudden changes in direction increase your risk of certain injuries. Dynamic movements put stress on joints, ligaments, and tendons, making them more likely to suffer from stress fractures, ligament sprains, and strains.
6. Mitigation Strategies: Maintaining physical fitness through regular exercise and conditioning is important to reduce the risk of injury. Proper use of protective equipment and adherence to warm-up and cool-down routines are important precautions. Being aware of the demands associated with certain activities and practicing safe methods can help prevent injuries.
Which part of the body is most often get sport injury?
Sports injuries can affect any part of the body. The most commonly affected are:
Achilles tendon: The Achilles tendon is a thick cord that connects the back of the lower leg (calf) to the heel. Helps you walk. However, the tendon may become swollen, inflamed, or stiff. It may break. This is called Achilles tendonitis or Achilles tendon rupture.
Ankle: The leg and foot join at the ankle. It contains three joints and several bones, cartilage, ligaments, muscles, and tendons. Ankle pain is often caused by an ankle sprain.
Elbow: The elbow is a joint that acts as a hinge between the upper arm and forearm. People often experience elbow pain due to repetitive motion or overuse (such as tennis elbow or Little League elbow).
Head: The head includes the face, skull, and brain. One of the most common head injuries is a concussion.
Knee: The knee is a complex joint that acts as a hinge between the upper and lower legs. Contains bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons. Knee pain can be caused by jumper’s knee or runner’s knee. Other common injuries include meniscal tears and anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears.
Shoulder: The shoulder connects the upper arm to the center of the body. It contains the rotator cuff, a group of muscles and tendons that hold the upper arm in the shoulder socket. Rotator cuff tendonitis and rotator cuff tears are common sports injuries.
Symptoms of Sport Injury
- Pain: Persistent or acute pain at the site of injury is a common symptom.
- Swelling: The affected area may show signs of swelling indicating inflammation and tissue damage.
- Bruising: Visible discoloration and bruising may occur due to bleeding under the skin from the injury.
- Limited range of motion: It may be difficult to move the injured body part through its full range of motion.
- Weakness: Weakness in the affected area is particularly noticeable during stress or use and may be a symptom.
- Sensitivity: Increased tenderness and sensitivity when touching the injured area.
- Instability: A feeling of instability or that the joints or muscles are not properly supported.
- Numbness or tingling: Numbness or tingling. Indicates possible neurological disorder.
- Visible deformity: In severe cases, there may be visible deformity or displacement of the affected area.
- Difficulty Bearing Weight: Attempting to put weight on the injured limb causes pain or discomfort.
Functional Difficulty: Impairment in the ability to perform normal activities or - sports movements Stiffness: Stiffness of an affected joint or muscle, especially after a period of inactivity.
Popping or Clicking Sounds: If you hear popping or clicking sounds during operation, this may indicate certain injuries. - Changes in Skin Color or Temperature: Changes in skin color (pale or bluish) or temperature (feeling cold) can indicate a problem with your circulatory system.
- Dizziness or Headache: Symptoms associated with a head injury, such as dizziness, headache, or altered consciousness.
How Sport Injury treated in Mancherial?
- Rest and Home Strategies:
Mild injuries respond well to rest, ice, compression, and elevation.
Commonly seen in mild sprains, bruises, and contusions. - Immobilization:
Use of a cast, splint, sling, or walking boot to restrict movement.
Particularly essential for stabilizing the healing of fractures and severe sprains. - Injection:
Corticosteroid injection to reduce inflammation and pain.Administered for certain conditions such as joint inflammation and bursitis.
- Prescription Medications: Prescription anti-inflammatory medications for more effective pain and inflammation management.
Usually a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). - Surgery: A surgical procedure to correct fractures and repair torn ligaments, tendons, or cartilage.
Common in procedures such as ACL reconstruction and fracture fixation. - Physical Therapy:Rehabilitation and strengthening of injured body parts through exercise and stretching exercises.
Essential for post-operative rehabilitation and treatment of muscle imbalances. - Braces and Supports: Recommendations for braces or supports to increase stability during healing.
Commonly seen with ligament injuries (such as knee braces) or sprains. - Activity Modification: Adjustment or modification of activity to reduce stress on the injured area.
Essential to prevent further damage and promote recovery. - RICE Protocol: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation for Treatment of Acute Injuries.
Use immediately after an injury such as a sprain or strain.


